고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문

앱 개발에 있어서 가장 많이 사용되는 디자인 요소 중 하나가 바로 백드롭 (Backdrop), 바텀시트(Bottom Sheet) 입니다. 스크린 이동을 시키지 않고, 바로 뜨는 화면에서 쉽게 동작을 이끌어내거나 주의를 끌 수 있기 때문인데요. 오늘은 이러한 기능을 구현하기 위한 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
들어가며: 백드롭(Backdrop)이란?
백드롭이란 (아래 그림과 같이) 기존의 스크린 위에 새로운 화면이 뜨는 방식의 UI를 뜻합니다. 인스타그램의 프로필 스크린에서 프로필 이름을 누르거나, 옵션을 누를 때 아래에서 올라오는 스크린을 말하는 것이죠. 아래에서 올라오는 화면이라는 의미로 바텀 시트라고 부르기도 합니다.
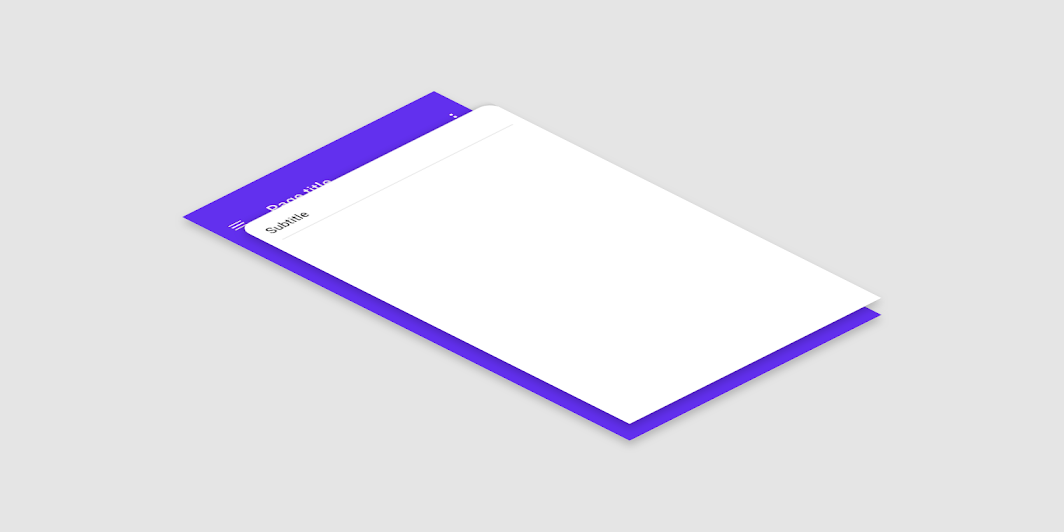
방법1: 라이브러리 활용하기
새로운 기능을 써야할 때 가장 편리한 방법은 라이브러리를 활용하는 것입니다. 검색하다가 몇가지 라이브러리를 찾을 수 있었는데요. 제공하는 기능도 많고 좋아보였는데, 다운로드 수가 적은 것이 조금 걱정이더라고요.
- react-native-gesture-bottom-sheet
- react-native-raw-bottom-sheet
만약 스크롤 유무 등을 선택할 수 있는 다양한 형태의 백드롭을 활용한다면 라이브러리를 활용하는 것을 추천드립니다. 다만 저는 스크롤 없이 열렸다 닫히는 백드롭만 사용할 예정이라서, 라이브러리를 활용하지 않고 직접 개발했습니다.
방법2: 직접 개발하기
아래는 스크롤 기능은 빼고, 하단에서 스르륵 올라왔다가 내려가는 애니메이션이 추가된 백드롭 컴포넌트입니다. 백드롭이 생성되었을 때 배경화면을 얼마나 흐리게 할 것인지 등은 아래 style에서 직접 설정하시면 됩니다!
import React, {
ReactNode,
useCallback,
useEffect,
useMemo,
useRef,
useState
} from 'react'
import {
Animated,
BackHandler,
Dimensions,
LayoutChangeEvent,
Pressable,
StyleProp,
StyleSheet,
View,
ViewStyle
} from "react-native"
interface BackdropProps {
visible: boolean
children: ReactNode
onClickClose?: () => void
afterOpen?: () => void
afterClose?: () => void
closeOnBackButton?: boolean
backdropStyle?: StyleProp<ViewStyle>
containerStyle?: StyleProp<ViewStyle>
}
const { height } = Dimensions.get('window');
const Backdrop = ({
visible,
children,
onClickClose = () => {},
afterOpen = () => {},
afterClose = () => {},
closeOnBackButton = false,
backdropStyle = {},
containerStyle = {}
}: BackdropProps) => {
const [contentHeight, setContentHeight] = useState(0);
const transitionY = useRef(new Animated.Value(height));
const animationConfig = {
useNativeDriver: true,
duration: 50,
speed: 14,
bounciness: 4,
}
const animationStart = useCallback(() => {
Animated.spring(
transitionY.current,
{
toValue: 0,
...animationConfig,
}
).start(() => afterOpen());
}, [afterOpen]);
const animationEnd = useCallback(() => {
Animated.spring(
transitionY.current,
{
toValue: contentHeight,
...animationConfig,
}
).start(() => afterClose());
}, [contentHeight, afterClose]);
const onLayout = (event: LayoutChangeEvent) => {
if (!contentHeight || !visible) {
transitionY.current.setValue(event.nativeEvent.layout.height);
setContentHeight(event.nativeEvent.layout.height);
}
};
const clampedTransition = useMemo(
() =>
transitionY.current.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, contentHeight || 1],
outputRange: [
contentHeight > height ? contentHeight - height : 0,
contentHeight || 1,
],
extrapolate: 'clamp',
}),
[contentHeight],
);
const clampedOpacity = useMemo(
() =>
transitionY.current.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, contentHeight || 1],
outputRange: [1, 0],
extrapolate: 'clamp',
}),
[contentHeight],
);
const clampedContentOpacity = useMemo(
() =>
transitionY.current.interpolate({
inputRange: [
0,
contentHeight ? contentHeight / 1.1 : 0.95,
contentHeight || 1,
],
outputRange: [1, 1, 0],
extrapolate: 'clamp',
}),
[contentHeight],
);
const handleClose = () => {
onClickClose()
return true
}
useEffect(() => {
if (visible) {
animationStart()
} else {
animationEnd()
}
}, [visible, animationStart, animationEnd]);
useEffect(() => {
if (closeOnBackButton) {
BackHandler.addEventListener('hardwareBackPress', handleClose);
}
return () => {
if (closeOnBackButton) {
BackHandler.removeEventListener('hardwareBackPress', handleClose);
}
}
}, [closeOnBackButton, handleClose]);
return (
<View pointerEvents="box-none" style={styles.wrapper}>
<Animated.View
style={[
styles.overlayStyle,
backdropStyle,
{
opacity: clampedOpacity,
},
]}
pointerEvents={visible ? 'auto' : 'none'}
>
<Pressable
style={styles.overlayTouchable}
onPress={handleClose}
/>
</Animated.View>
<Animated.View
pointerEvents="box-none"
accessibilityLiveRegion="polite"
style={[
styles.contentContainer,
{
transform: [
{
translateY: clampedTransition,
},
],
opacity: clampedContentOpacity,
},
]}>
<View
style={containerStyle}
onLayout={onLayout}
>
{children}
</View>
</Animated.View>
</View>
)
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
wrapper: {
position: 'absolute',
left: 0,
right: 0,
top: 0,
bottom: 0,
zIndex: 100,
elevation: 10,
justifyContent: 'flex-end',
flex: 1,
},
overlayTouchable: {
flex: 1,
},
contentContainer: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'flex-end',
},
overlayStyle: {
position: 'absolute',
left: 0,
right: 0,
top: 0,
bottom: 0,
backgroundColor: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)'
},
})
export default Backdrop
그리고 이러한 Backdrop 컴포넌트를 이용할 때에는 아래와 같이 컴포넌트를 import하여 내부에 원하는 형태의 컴포넌트를 구성하면 됩니다. (그리고 뒤로가기를 눌렀을 때 닫히게 만들고 싶은 경우가 많아서 closeOnBackButton props도 추가하였습니다)
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import {
View,
Pressable,
Text
} from 'react-native'
import Backdrop from 'src/components/Backdrop' // 컴포넌트를 만든 경로에서 import
const TestScreen = () => {
const [isBackdropOpened, setIsBackdropOpened] = useState(false)
return (
<View>
<Pressable onPress={() => setIsBackdropOpened(true)}>
<Text>백드롭 열기</Text>
</Pressable>
<Backdrop
visible={isBackdropOpened}
onClickClose={() => setIsBackdropOpened(false)}
closeOnBackButton
containerStyle={{ backgroundColor: '#ffffff' }}
>
<View>
<Text>
짜잔!
</Text>
</View>
</Backdrop>
</View>
)
}
export default TestScreen
오늘은 백드롭 구현에 대해 한 번 살펴보았는데요. 콘텐츠가 도움이 되었길 바라며, 그럼 오늘도 모두들 해피코딩하세요 :)
'개발' 카테고리의 다른 글
| react-native에서 뒤로가기 구현하기 (BackHandler) (0) | 2022.02.04 |
|---|---|
| react native 에서 그림자 구현하기 (w/ react-native-shadow) (0) | 2022.02.03 |
| position sticky 깨지는 이슈! sticky 사용 전 필수 상식 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
| position fixed 깨지는 이슈! fixed 사용 전 필수 상식 (0) | 2022.02.01 |
| react-query 캐싱 이슈 해결하기! 변경, 삭제할 때 쿼리 업데이트가 안된다? (0) | 2022.01.31 |


댓글 영역